The Capacitor in an AC Circuit
A capacitor in an AC circuit is acting as a capacitive AC resistor. It blocks direct current (DC), while alternating current (AC) can pass.
Example: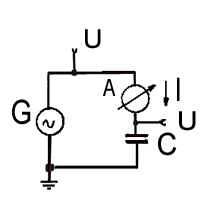 The current ' I ' can be calculated in the following way:
The current ' I ' can be calculated in the following way:
U
I = ------
Xc
with
1
Xc = -----------
2 pi f C
|
Xc = capacitive AC resistance of
the capacitor, in Ohm
pi = 3.1416
f = Frequency of the current in Hertz [Hz]
C = Capacity of the capacitor in Farad [F]
U = Voltage in Volt [V]
I = Current in Ampere [A]
G = AC generator with frequency f and
output voltage U
Xc is the capacitive AC resistance in Ohm. For DC ( f = 0 )
it is infinite large and for AC the value of Xc lowers to finite values, depending on the frequency f.This means , direct current is blocked by the capacitor while alternating current can pass, more or less, depending on the frequency. High frequency current can pass more easy than low frequency current.
In the following a calculated example with frequencies from 50 Hz to 100 kHz.
Example for C = 1 µF ; U = 1 Volt :
f [Hz] 50 Hz 100 Hz 1 kHz 10 kHz 100 kHz
-------------------------------------------
Xc [Ohm] 3183 1592 159 15.9 1.6 Ohm
-------------------------------------------
I [mA] 0.314 0.63 6.3 63 630 mA
-------------------------------------------